# Countries
 Most entries in a data catalog will relate to one or multiple countries.
All metadata standards and schemas used by NADA include an element to
capture this information:
Most entries in a data catalog will relate to one or multiple countries.
All metadata standards and schemas used by NADA include an element to
capture this information:
'nation' in the DDI Codebook;
'geographic_units' in the time series schema;
'ref_country' in the Dublin Core/document schema and in the tables schema;
'locationsShown/countryName' in the IPTC schema for images;
'country' in the video schema.
This information, especially in multi-country catalogs, is particularly relevant to filter data. By default, NADA provides a facet to filter entries by country.
But countries can be named in different manners in datasets/metadata. For example, the Democratic Republic of Congo could also be referred to as "DR Congo", "Congo, DR", "DRC". Multiple variants of a country name should all be mapped to a unique label, for two reasons:
It would be inconvenient to users of a catalog to have to select more than one item in a list to identify entries related to one single country.
It can be politically important (and a requirement) for some organizations to comply with specific names for countries and territories.
To address this issue, catalog administrators can provide their instance of NADA with a reference list of countries and capture the alternative names that may be found in the metadata. Note that "countries" can be "territories", "economies", "regions", or groups of countries. A default list of country names is provided in the NADA application, which can be edited.
# Using the administrator interface
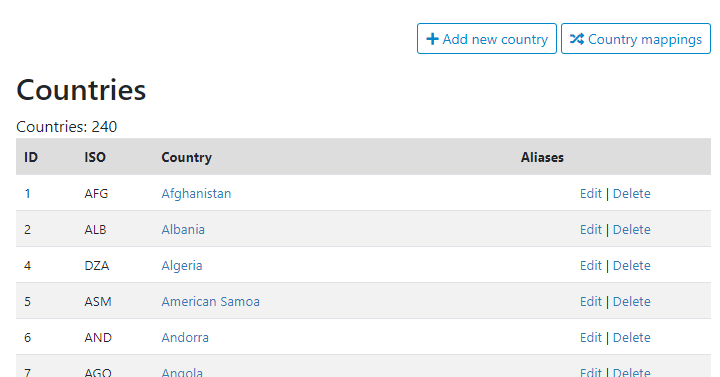
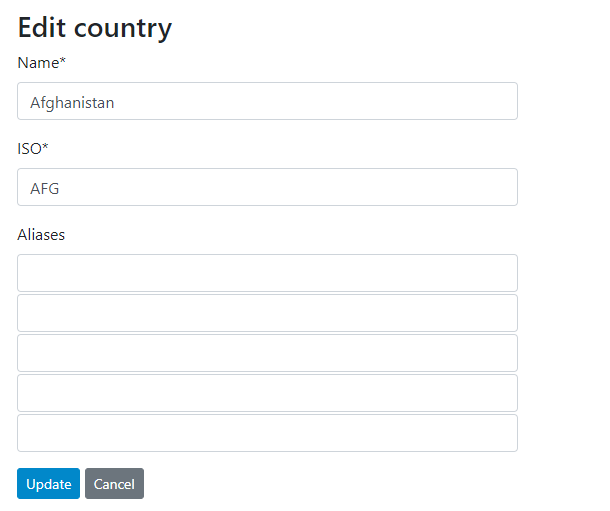
To add a new country, click "Add new country". To edit a country, click on "Edit". In both cases, you will be taken to a form where the country name to be used as the reference, its code (ISO, or possibly other), and the variants of the country name (aliases), can be entered or edited.
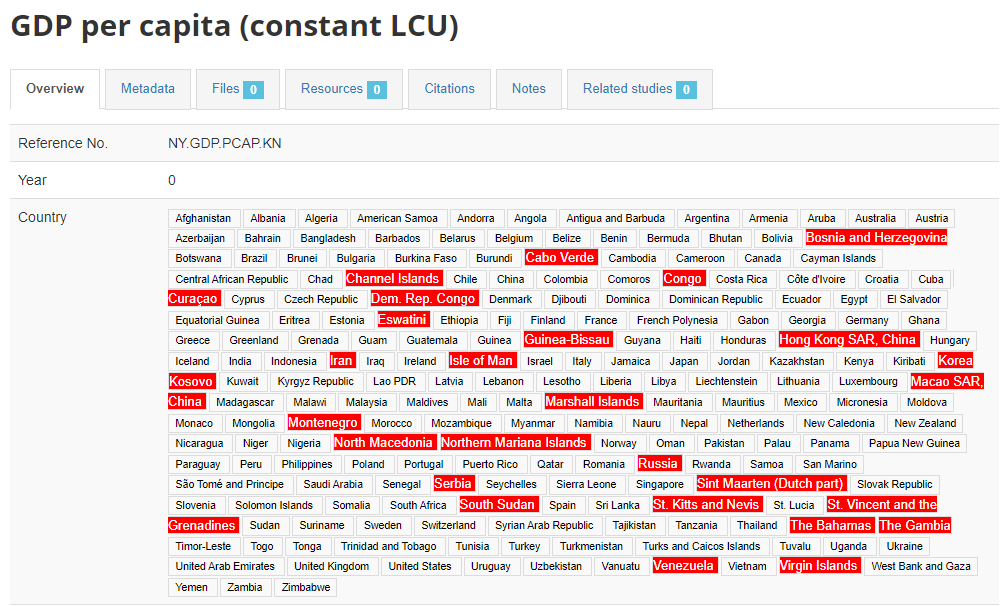
The list of countries entered in this list will serve as a control list for metadata entered in NADA. When metadata are imported and contain non-compliant names, these non-compliant names will be flagged in the entry page (displayed with red background). In the example below, "Cabo Verde" for example is flagged because the reference list of countries only recognizes the name "Cape Verde". Ideally, these issues should be fixed.
The names do NOT have to be fixed by changing the metadata themselves. In some cases, it would make sense to do so, but in others it could create inconsistencies between the source data and the metadata. The solution to address the issue when the data/metadata cannot be changed is to map non-compliant names to names found in the reference list. The fixes (i.e. the aliases for country names) will be stored, so the chances of finding non-compliant names in metadata is likely to rapidly reduce over time.
Clicking on any flagged name, or on the main menu item Settings > Countries, will open the page where the mappings can be done. In that page, click on "Country mappings".
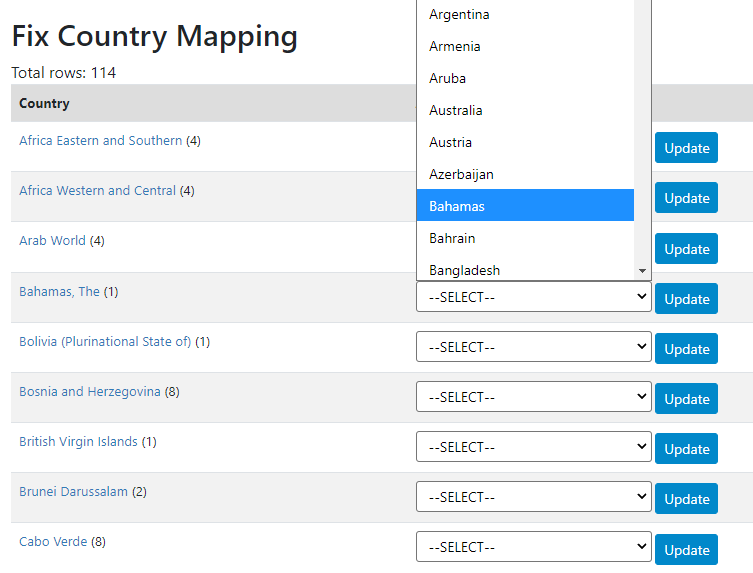
This will open a table showing the list of non-compliant country names. For each one of them, you can select a country from the list of compliant countries, then click "Update". The non-compliant name will now be stored as an alias which will be applied automatically to other datasets that may have used the same non-compliant name. This line of the table will disappear when refreshing the page.
If you do not find an equivalent in the reference list, you may consider adding it. This is however not a requirement. Metadata with non-compliant country names can be stored in the application. The main impact is that they will not be identified in the filter by country (facet), which only shows the countries found in the reference list as options.
Warning: if you delete a country ...
# Using the API
Uploading and maintaining a list of countries
R
Python